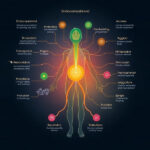
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a complex cell-signaling system that plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis within the body. While it is widely recognized for its influence on pain, mood, and immune responses, recent research has illuminated its significant impact on metabolic processes, including appetite regulation, energy balance, and fat storage.
The Role of the ECS in Metabolism
The ECS comprises endocannabinoids, cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2), and metabolic enzymes. CB1 receptors, primarily located in the brain and central nervous system, are particularly influential in regulating appetite and energy expenditure. When activated, these receptors can stimulate hunger and promote fat storage, while also influencing how the body processes energy.
Conversely, CB2 receptors, found mainly in the peripheral tissues and immune system, play a role in regulating inflammation and metabolic health. The balance between these receptors is crucial for maintaining a healthy metabolism.
Appetite Regulation
One of the most well-known functions of the ECS is its role in appetite regulation. Endocannabinoids, particularly anandamide, can enhance the pleasure associated with eating, leading to increased food intake. This mechanism is particularly relevant in the context of obesity, where dysregulation of the ECS may contribute to overeating and weight gain.
Energy Balance
The ECS also influences energy balance by modulating how the body stores and utilizes energy. Studies have shown that cannabinoids can affect insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. For instance, research indicates that individuals with obesity may have altered ECS activity, which can lead to insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome.
Fat Storage
The ECS plays a role in determining how the body stores fat. Activation of CB1 receptors can promote lipogenesis (the process of converting carbohydrates into fat), while blocking these receptors may enhance fat breakdown. This dual role suggests that targeting the ECS could provide therapeutic strategies for managing obesity and metabolic disorders.
Implications for Obesity and Metabolic Disorders
The implications of cannabinoid interactions with the ECS for obesity and metabolic disorders are profound. Recent studies have shown that certain cannabinoids, such as CBD (cannabidiol), may help improve metabolic health by reducing appetite and promoting fat oxidation. Additionally, research has indicated that modulating ECS activity could help combat insulin resistance and improve overall metabolic function.
Recent Findings
Recent studies have explored the potential of cannabinoid-based therapies in addressing obesity and metabolic disorders. For example, a study published in the journal Obesity found that CBD administration led to reduced body weight and improved metabolic markers in animal models. Another study highlighted the potential of ECS modulation in enhancing insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation, key factors in metabolic health.
Conclusion
The endocannabinoid system is a vital player in regulating metabolism, influencing appetite, energy balance, and fat storage. As research continues to unfold, the ECS presents exciting opportunities for developing novel therapeutic approaches to combat obesity and metabolic disorders. Understanding the intricate relationship between cannabinoids and metabolic processes may pave the way for innovative treatments that promote better health and well-being. As we delve deeper into this fascinating field, the potential for cannabinoid-based interventions in metabolic health becomes increasingly promising.